Embark on an exploration of limiting reactants and percent yield through the lens of our comprehensive Limiting Reactant Percent Yield Worksheet. This invaluable resource provides a profound understanding of these fundamental concepts in chemistry, guiding you through the intricacies of chemical reactions and their outcomes.
Delve into the concept of limiting reactants, their identification, and their pivotal role in determining the extent of reactions. Unravel the mysteries of percent yield, its calculation, and the factors that influence its value. Witness the intricate interplay between limiting reactants and percent yield, unlocking the secrets of stoichiometry and its predictive power.
Limiting Reactant
A limiting reactant is a reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction, limiting the amount of product that can be formed. In other words, the limiting reactant determines the maximum amount of product that can be obtained from a given set of reactants.
For example, consider the following reaction:
CH4+ 2O 2→ CO 2+ 2H 2O
In this reaction, methane (CH 4) and oxygen (O 2) are the reactants, and carbon dioxide (CO 2) and water (H 2O) are the products. If we start with 1 mole of CH 4and 2 moles of O 2, the CH 4will be the limiting reactant because it will be completely consumed before all of the O 2is used up.
To identify the limiting reactant in a given reaction, we can use the following steps:
- Balance the chemical equation.
- Convert the given amounts of reactants to moles.
- Divide the number of moles of each reactant by its stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced equation.
- The reactant with the smallest mole ratio is the limiting reactant.
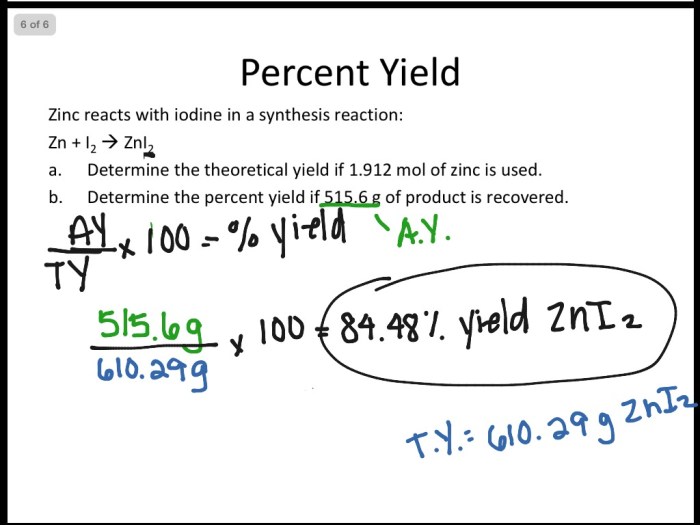
Percent Yield
Percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a chemical reaction. It is defined as the ratio of the actual yield of a product to the theoretical yield, multiplied by 100%.
The theoretical yield is the maximum amount of product that can be obtained from a given set of reactants, based on the stoichiometry of the reaction. The actual yield is the amount of product that is actually obtained in the reaction.
To calculate percent yield, we can use the following formula:
Percent yield = (Actual yield / Theoretical yield) x 100%
For example, if we obtain 10 grams of CO 2from the reaction between 1 mole of CH 4and 2 moles of O 2, and the theoretical yield is 22 grams of CO 2, the percent yield is:
Percent yield = (10 grams / 22 grams) x 100% = 45.5%
There are a number of factors that can affect percent yield, including:
- The purity of the reactants
- The reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, etc.)
- The presence of catalysts or inhibitors
- Side reactions
Limiting Reactant and Percent Yield
The limiting reactant has a direct impact on the percent yield of a chemical reaction. The limiting reactant determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed, so if the limiting reactant is used up, the reaction will stop and no more product will be formed.
For example, if we start with 1 mole of CH 4and 1 mole of O 2, the O 2will be the limiting reactant because it will be completely consumed before all of the CH 4is used up. This means that the maximum amount of CO 2that can be formed is 1 mole, and the percent yield will be 100%.
However, if we start with 2 moles of CH 4and 1 mole of O 2, the CH 4will be the limiting reactant because it will be completely consumed before all of the O 2is used up. This means that the maximum amount of CO 2that can be formed is 1 mole, and the percent yield will be 50%.
Therefore, it is important to identify the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction in order to predict the percent yield.
Helpful Answers: Limiting Reactant Percent Yield Worksheet
What is the significance of identifying the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction?
Identifying the limiting reactant is crucial as it determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed. It helps predict the reaction’s extent and prevents excess reactants from being wasted.
How does percent yield reflect the efficiency of a chemical reaction?
Percent yield measures the ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield, indicating how effectively the reactants are utilized. It provides insights into reaction efficiency and potential areas for optimization.
Can the limiting reactant concept be applied to reactions involving multiple reactants?
Yes, the limiting reactant concept applies to reactions with multiple reactants. By comparing the mole ratios of reactants to their stoichiometric coefficients, the limiting reactant can be identified, and its presence governs the reaction’s progress.
