With prokaryotes and eukaryotes answer key at the forefront, this comprehensive guide unravels the fundamental differences between these two distinct cell types. From their structural components to their evolutionary history, we delve into the fascinating world of cellular biology, providing a thorough understanding of the key characteristics that set prokaryotes and eukaryotes apart.
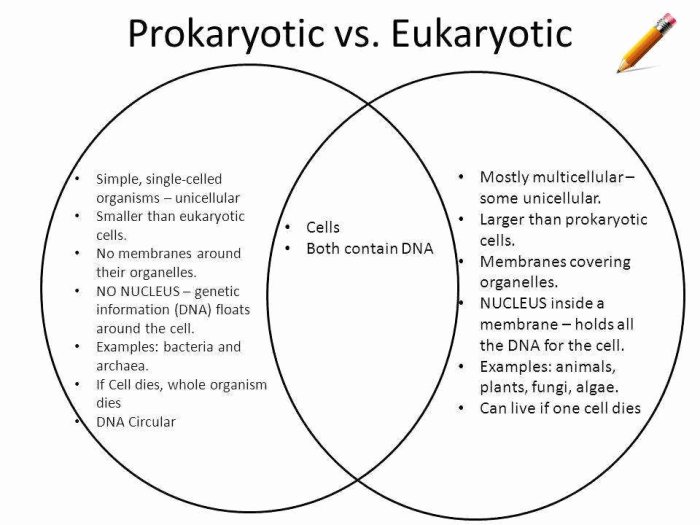
Prokaryotes, the simpler and more ancient cell type, lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes possess a more complex structure, including a nucleus and various membrane-bound organelles. This structural distinction has profound implications for their cellular functions, reproductive processes, and evolutionary trajectories.
1. Definition and Overview
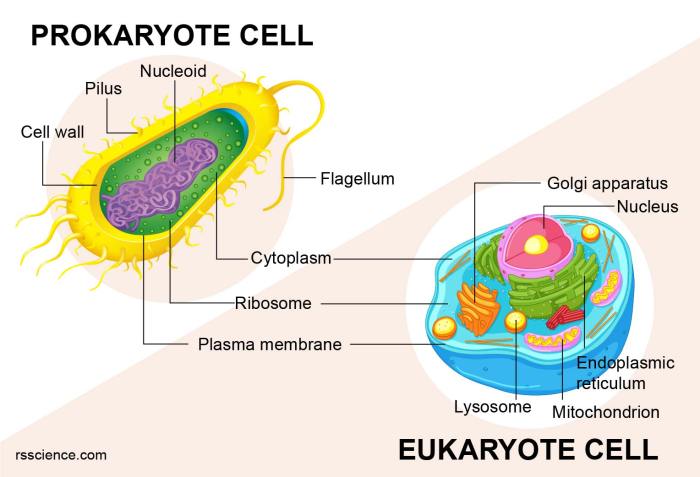
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are the two fundamental types of cells that exist in the biological world. Prokaryotes are simpler, single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes are more complex, multicellular organisms that possess a nucleus and a variety of membrane-bound organelles.
Comparative Table of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
| Characteristic | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Size | Typically 0.1-5.0 µm | Typically 10-100 µm |
| Complexity | Simple | Complex |
| Reproduction | Asexual (binary fission) | Asexual (mitosis) and sexual (meiosis) |
2. Structure and Organization
Prokaryotes
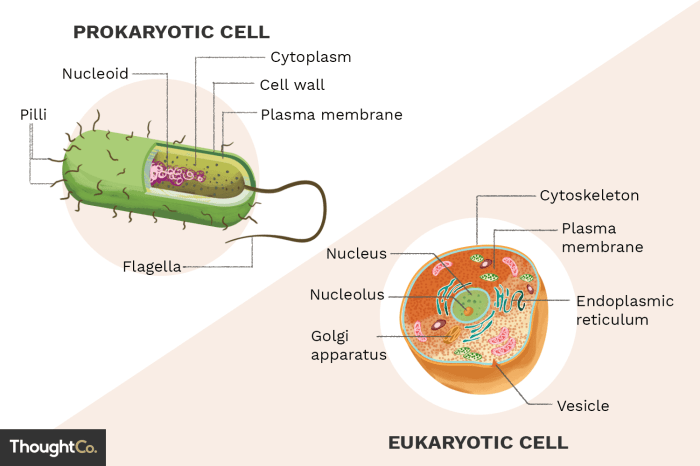
Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller and simpler in structure compared to eukaryotic cells. They lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Instead, their genetic material is concentrated in a region called the nucleoid. Prokaryotes also have a cell wall, a cell membrane, and ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis.
Eukaryotes
Eukaryotic cells are more complex and organized than prokaryotic cells. They have a true nucleus, which is surrounded by a nuclear membrane and contains the cell’s genetic material. Eukaryotes also possess a variety of membrane-bound organelles, including the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and lysosomes.
These organelles perform specialized functions, such as protein synthesis, modification, and energy production.
Diagram Illustrating Structural Differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
[Diagram atau ilustrasi yang menunjukkan perbedaan struktural antara prokariota dan eukariota.]
3. Reproduction
Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes reproduce asexually through binary fission, a process in which the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This process is relatively simple and rapid, allowing prokaryotes to multiply quickly.
Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes have more complex reproductive mechanisms. They can reproduce asexually through mitosis, which produces two identical daughter cells, or sexually through meiosis, which produces four haploid cells (gametes) that can fuse to form a zygote. Meiosis is essential for genetic diversity and the production of offspring with unique combinations of traits.
Table Comparing Reproductive Mechanisms of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
| Characteristic | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
|---|---|---|
| Reproduction | Asexual (binary fission) | Asexual (mitosis) and sexual (meiosis) |
| Number of daughter cells | 2 | 2 (mitosis) or 4 (meiosis) |
| Genetic variation | Low | High |
4. Evolutionary History
Prokaryotes are believed to be the oldest and most primitive form of life on Earth. They evolved approximately 3.5 billion years ago and have remained relatively unchanged over time. Eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes approximately 1.5 billion years ago through a process called endosymbiosis.
In this process, a prokaryotic cell engulfed another prokaryotic cell, which became an endosymbiont. Over time, the endosymbiont evolved into the membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells.
Timeline Illustrating Evolutionary Divergence of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
[Timeline atau ilustrasi yang menunjukkan divergensi evolusioner prokariota dan eukariota.]
5. Examples and Significance: Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes Answer Key
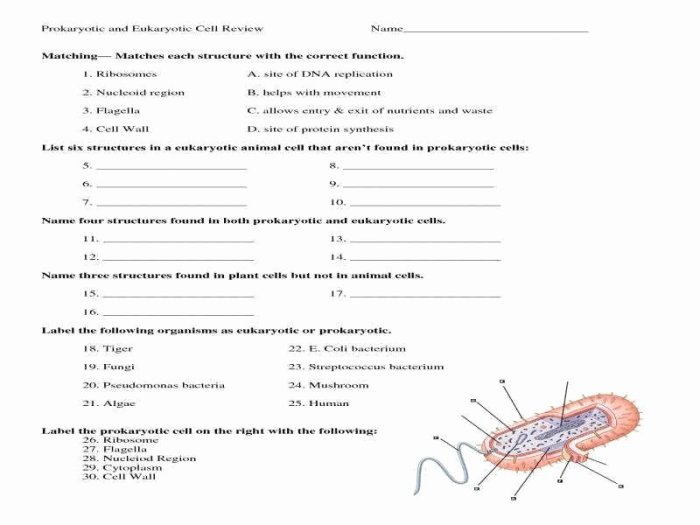
Examples of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
- Prokaryotes:Bacteria, archaea
- Eukaryotes:Plants, animals, fungi, protists
Ecological Roles of Prokaryotes
- Nutrient cycling: Prokaryotes play a crucial role in nutrient cycling by decomposing organic matter and releasing nutrients back into the environment.
- Biotechnology: Prokaryotes are used in a variety of biotechnological applications, such as the production of antibiotics and enzymes.
Significance of Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and eukaryotes answer key
- Multicellularity: Eukaryotes are capable of forming multicellular organisms, which allows for greater complexity and specialization.
- Tissue specialization: Eukaryotic cells can differentiate into specialized tissues, such as muscle, nerve, and epithelial tissues, which perform specific functions.
- Human health: Eukaryotes are essential for human health, as they make up the human body and are involved in a variety of physiological processes.
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
The presence of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes, which are absent in prokaryotes.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Asexual reproduction through binary fission.
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
The theory that eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship between prokaryotic cells.