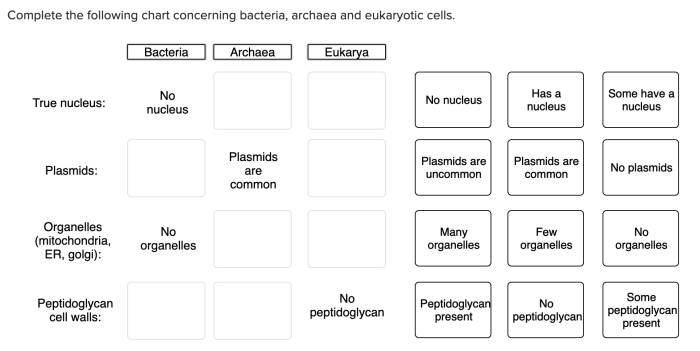
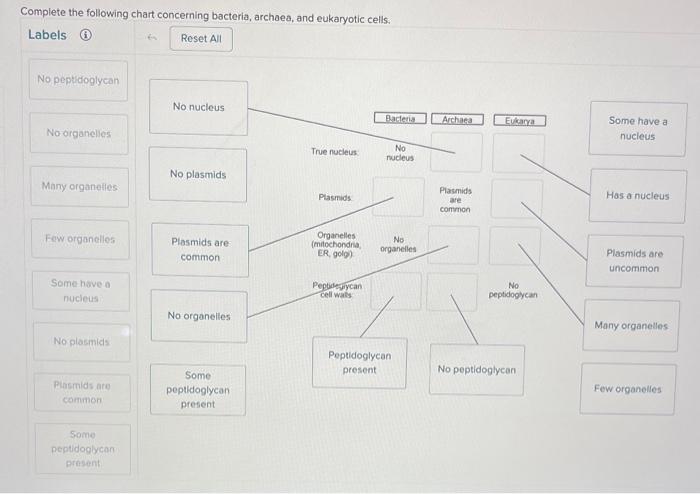
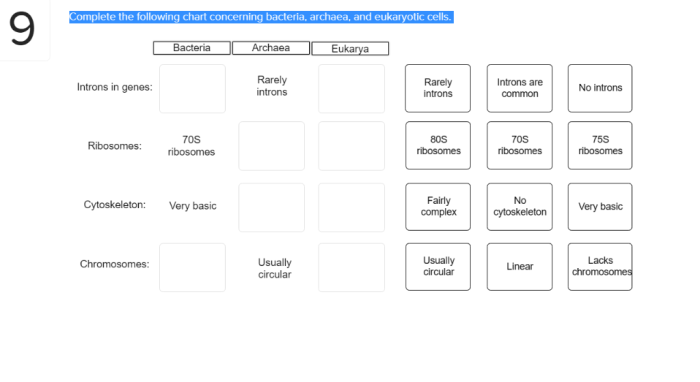
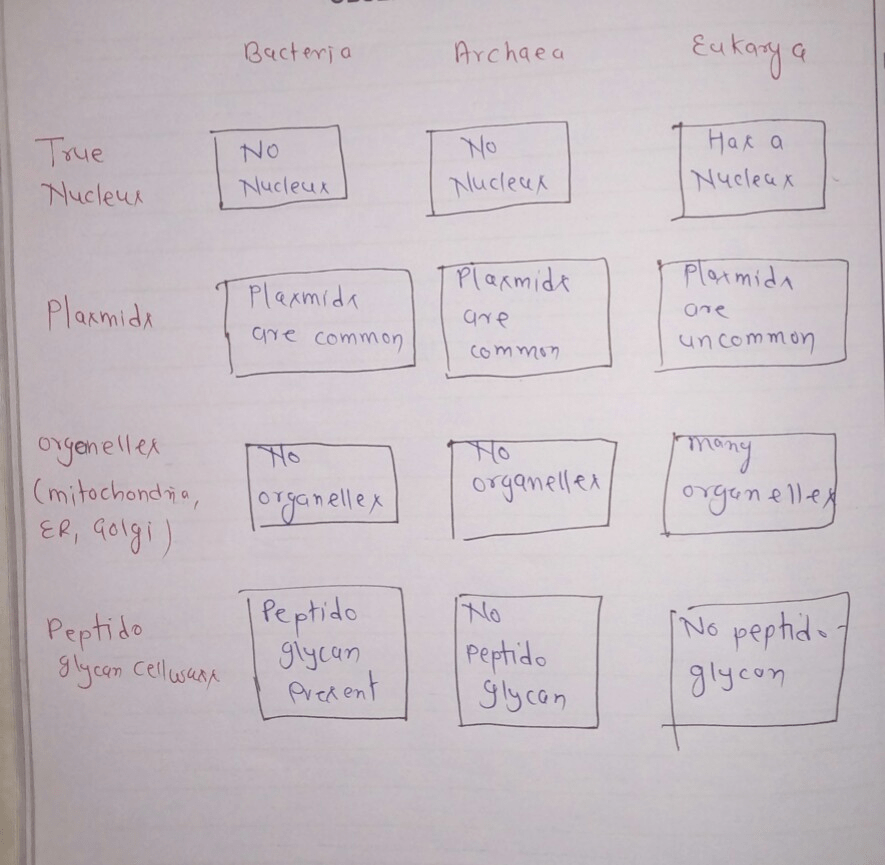
Complete the following chart concerning bacteria archaea and eukaryotic cells – Complete the following chart concerning bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotic cells sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
This comprehensive guide delves into the structural differences, genetic material organization, reproductive mechanisms, metabolic pathways, evolutionary relationships, and practical applications of these diverse cell types, providing a holistic understanding of their unique characteristics and contributions to the biological world.
Cell Structure
Bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotic cells exhibit distinct structural differences that reflect their evolutionary divergence and functional adaptations.
Cell Wall
- Bacteria: Peptidoglycan (gram-positive) or lipopolysaccharide (gram-negative)
- Archaea: Pseudomurein or S-layer proteins
- Eukaryotes: Absent (except for plant cell walls)
Cell Membrane, Complete the following chart concerning bacteria archaea and eukaryotic cells
- Bacteria: Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
- Archaea: Phospholipid bilayer with ether-linked lipids and isoprenoids
- Eukaryotes: Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, glycolipids, and cholesterol
Cytoplasm
- Bacteria: Contains ribosomes, DNA, and other organelles
- Archaea: Contains ribosomes, DNA, and unique organelles
- Eukaryotes: Contains ribosomes, DNA, organelles enclosed by membranes, and a cytoskeleton
Organelles
| Organelle | Bacteria | Archaea | Eukaryotes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Absent | Present |
| Nucleolus | Absent | Absent | Present |
| Ribosomes | 70S | 70S | 80S (cytoplasm) and 70S (mitochondria) |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Absent | Present |
| Chloroplasts | Absent | Absent | Present (in plant cells) |
FAQ Guide: Complete The Following Chart Concerning Bacteria Archaea And Eukaryotic Cells
What is the key difference between bacteria and archaea?
Bacteria and archaea are both prokaryotic cells, but they differ in their cell wall composition, genetic material organization, and metabolic pathways.
How do eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells possess a true nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and a more complex cellular structure compared to prokaryotic cells, which lack these features.
What are the different mechanisms of reproduction in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotic cells?
Bacteria and archaea reproduce asexually through binary fission, while eukaryotic cells can reproduce both asexually (through mitosis) and sexually (through meiosis and fertilization).