Arrange the atomic analysis methods in order of increasing sensitivity – Atomic analysis methods, a diverse array of techniques, empower scientists to probe the elemental composition of matter with unparalleled precision. Their applications span a multitude of disciplines, from environmental monitoring to medical diagnostics. This article presents a comprehensive overview of atomic analysis methods, categorizing them based on their sensitivity, a crucial parameter that dictates their analytical capabilities.
The sensitivity of an atomic analysis method quantifies its ability to detect and measure the presence of specific elements in a sample. Factors influencing sensitivity include the method’s inherent detection limits, sample preparation techniques, and instrumentation capabilities. Understanding the sensitivity hierarchy of atomic analysis methods is paramount for selecting the most appropriate technique for a given analytical task.
Overview of Atomic Analysis Methods

Atomic analysis methods are a set of analytical techniques used to determine the elemental composition and structure of materials at the atomic level. These methods provide detailed information about the types and concentrations of elements present in a sample, as well as their chemical states and bonding arrangements.
Atomic analysis methods find applications in various fields, including environmental monitoring, materials science, forensics, and medical diagnostics. They enable researchers and scientists to gain insights into the composition, properties, and behavior of materials, helping to advance scientific knowledge and technological developments.
Types of Atomic Analysis Methods

- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS): AAS measures the absorption of light by atoms in a sample. It is a widely used technique for determining the concentration of specific elements in various matrices.
- Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (AES): AES measures the emission of light by atoms in a sample when they are excited by an energy source. It is used to determine the elemental composition and quantify the concentration of elements in a sample.
- Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS): ICP-MS is a highly sensitive technique that combines an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) with a mass spectrometer. It allows for the simultaneous determination of multiple elements in a sample with high accuracy and precision.
- X-ray Fluorescence (XRF): XRF is a non-destructive technique that uses X-rays to excite atoms in a sample. It is commonly used for elemental analysis in various materials, including solids, liquids, and powders.
- Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA): NAA is a nuclear technique that involves irradiating a sample with neutrons and measuring the subsequent gamma radiation emitted by the activated atoms. It is a highly sensitive method for determining trace elements in a sample.
Sensitivity of Atomic Analysis Methods: Arrange The Atomic Analysis Methods In Order Of Increasing Sensitivity
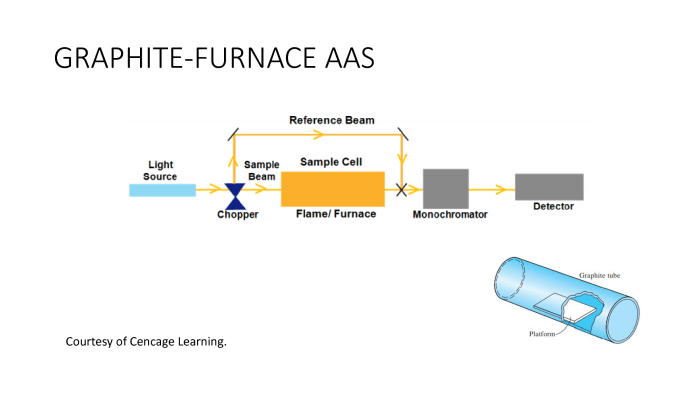
Sensitivity in the context of atomic analysis methods refers to the ability to detect and quantify elements in a sample at low concentrations. The sensitivity of a method is determined by various factors, including:
- Sample preparation: Proper sample preparation techniques can minimize interferences and enhance the signal-to-noise ratio, improving sensitivity.
- Instrumentation: The design and performance of the analytical instrument, including its optics, detectors, and data acquisition systems, play a crucial role in determining sensitivity.
- Matrix effects: The presence of other elements in the sample can interfere with the analysis, affecting the sensitivity of the method.
- Detection limit: The detection limit is the lowest concentration of an element that can be reliably detected and quantified using a specific method.
Arranging Atomic Analysis Methods in Order of Increasing Sensitivity
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)
- Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (AES)
- X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
- Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
- Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA)
This order is based on the general sensitivity ranges of these methods, with NAA being the most sensitive and AAS being the least sensitive.
Applications of Atomic Analysis Methods
Atomic analysis methods have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Environmental monitoring: Analysis of air, water, and soil samples to determine elemental composition and identify pollutants.
- Materials science: Characterization of materials for elemental composition, purity, and structural analysis.
- Forensics: Analysis of evidence in criminal investigations, such as gunshot residue, trace metals, and elemental profiling.
- Medical diagnostics: Analysis of biological samples, such as blood, urine, and tissue, to determine elemental composition and identify biomarkers for diseases.
- Archaeology: Analysis of artifacts and archaeological materials to determine elemental composition and gain insights into historical events and cultural practices.
Limitations of Atomic Analysis Methods
While atomic analysis methods offer powerful tools for elemental analysis, they also have certain limitations:
- Sample preparation: Sample preparation can be time-consuming and complex, potentially introducing errors and affecting the accuracy of the analysis.
- Matrix effects: The presence of other elements in the sample can interfere with the analysis, leading to inaccurate results.
- Detection limits: Atomic analysis methods have detection limits, and certain elements may be below the detectable range.
- Cost and complexity: Some atomic analysis methods, such as ICP-MS and NAA, require specialized equipment and expertise, making them more expensive and complex to operate.
FAQ Insights
What factors influence the sensitivity of atomic analysis methods?
The sensitivity of atomic analysis methods is influenced by factors such as detection limits, sample preparation techniques, and instrumentation capabilities.
How is the sensitivity of atomic analysis methods determined?
The sensitivity of atomic analysis methods is typically determined by comparing their detection limits, which represent the lowest concentration of an element that can be reliably detected.
What are the applications of atomic analysis methods?
Atomic analysis methods find applications in various fields, including environmental monitoring, medical diagnostics, materials science, and forensic science.
