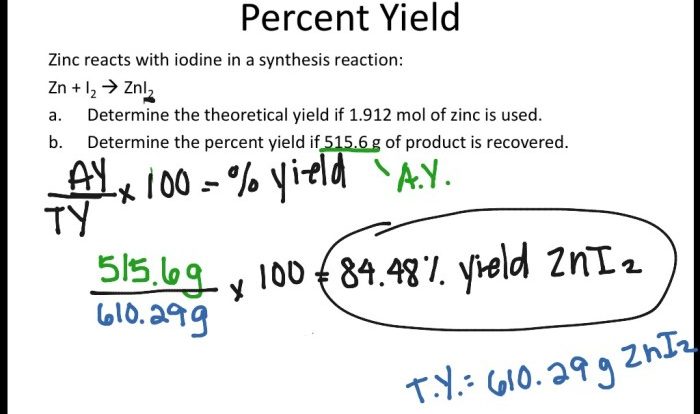
What is the mass percentage of o in c3h8o2 – What is the mass percentage of oxygen in C3H8O2? This question embarks us on a journey into the realm of chemistry, where we delve into the significance of mass percentage and unravel the intricacies of calculating the mass percentage of oxygen in C3H8O2, a compound with a rich tapestry of applications.
Mass percentage, a fundamental concept in chemistry, quantifies the relative abundance of an element within a compound. In the case of C3H8O2, understanding its mass percentage of oxygen is crucial for comprehending its chemical properties and behavior.
Mass Percentage of Oxygen in C3H8O2
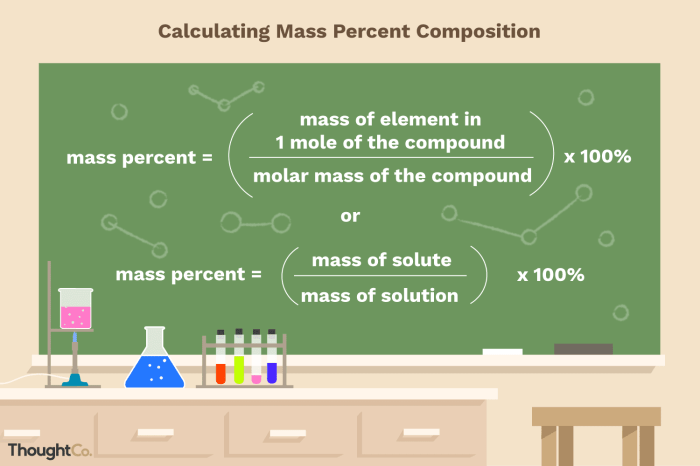
Mass percentage is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the relative amount of a specific element or compound within a substance. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including manufacturing, environmental science, and analytical chemistry.
In this article, we will explore the concept of mass percentage, particularly in the context of the compound C3H8O2, commonly known as propanol. We will delve into the formula and steps involved in calculating the mass percentage of oxygen in C3H8O2, its applications, and related concepts.
Calculating Mass Percentage of Oxygen
The mass percentage of an element in a compound is calculated using the following formula:
(Mass of Element / Molar Mass of Compound) x 100%
To calculate the mass percentage of oxygen in C3H8O2, we first need to determine its molar mass. The molar mass of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses of all its constituent atoms.
For C3H8O2, the molar mass is:
(12.01 g/mol) + 8(1.01 g/mol) + 2(16.00 g/mol) = 60.09 g/mol
Next, we need to find the mass of oxygen in C3H8O2. C3H8O2 contains two oxygen atoms, each with an atomic mass of 16.00 g/mol.
Therefore, the mass of oxygen in C3H8O2 is:
(16.00 g/mol) = 32.00 g/mol
Now we can plug these values into the mass percentage formula:
(32.00 g/mol / 60.09 g/mol) x 100% = 53.23%
Therefore, the mass percentage of oxygen in C3H8O2 is 53.23%.
Applications and Significance
Understanding the mass percentage of oxygen in C3H8O2 has practical applications in various fields:
- Chemistry:It helps determine the elemental composition of compounds, which is crucial for understanding their chemical properties and reactivity.
- Manufacturing:It plays a role in optimizing production processes, ensuring the desired composition of products, and meeting quality standards.
- Environmental Science:It aids in monitoring and controlling air and water pollution, as C3H8O2 is a volatile organic compound (VOC) that contributes to ozone formation.
Variations and Extensions, What is the mass percentage of o in c3h8o2
The mass percentage calculation can be applied to determine the mass percentage of any element in a compound. For example, we can calculate the mass percentage of carbon or hydrogen in C3H8O2 using the same formula.
Additionally, the mass percentage concept can be extended to related concepts such as empirical formula and molecular formula. The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound, while the molecular formula represents the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule.
By understanding the mass percentage and related concepts, we gain a deeper insight into the composition and properties of chemical compounds.
Question & Answer Hub: What Is The Mass Percentage Of O In C3h8o2
What is the significance of mass percentage in chemistry?
Mass percentage plays a pivotal role in chemistry as it allows us to determine the relative abundance of elements within a compound. This information is essential for understanding the compound’s chemical properties, reactivity, and behavior.
How is the mass percentage of oxygen in C3H8O2 calculated?
The mass percentage of oxygen in C3H8O2 can be calculated using the formula: (mass of oxygen / molar mass of C3H8O2) x 100%. The molar mass of C3H8O2 is determined by adding the atomic masses of each element multiplied by their respective number of atoms in the compound.