Simulation investigating reaction rates answer key opens the door to a realm of scientific inquiry, providing a powerful tool to unravel the complexities of chemical reactions. This guide delves into the fundamentals of simulation, exploring its role in understanding reaction rates and unraveling the factors that govern their behavior.
Through a series of carefully designed experiments, we will embark on a journey to uncover the secrets of reaction rates, harnessing the power of simulation to gain invaluable insights into the dynamic world of chemical kinetics.
Simulation Overview: Simulation Investigating Reaction Rates Answer Key
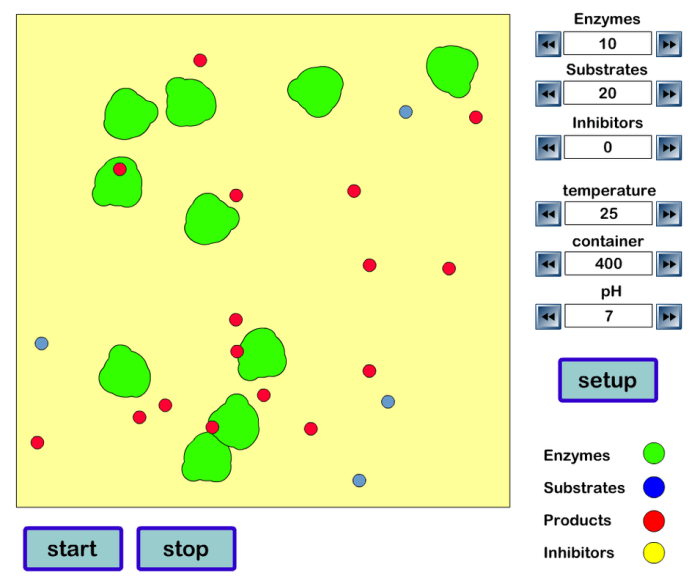
A simulation is a virtual representation of a real-world system that allows researchers to investigate complex processes without the need for physical experimentation. In the context of investigating reaction rates, simulations can provide insights into the factors that affect the rate of a reaction and the mechanisms by which they interact.
There are various types of simulations used to investigate reaction rates, including:
- Molecular dynamics simulations: These simulations model the interactions between individual molecules, providing detailed information about the reaction pathways and energy changes involved.
- Monte Carlo simulations: These simulations use random sampling to generate possible reaction pathways and estimate the probability of each pathway occurring.
- Kinetic Monte Carlo simulations: These simulations combine elements of molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations, allowing for the investigation of reactions on surfaces or in confined environments.
Factors Affecting Reaction Rates
The rate of a reaction is influenced by several factors, including:
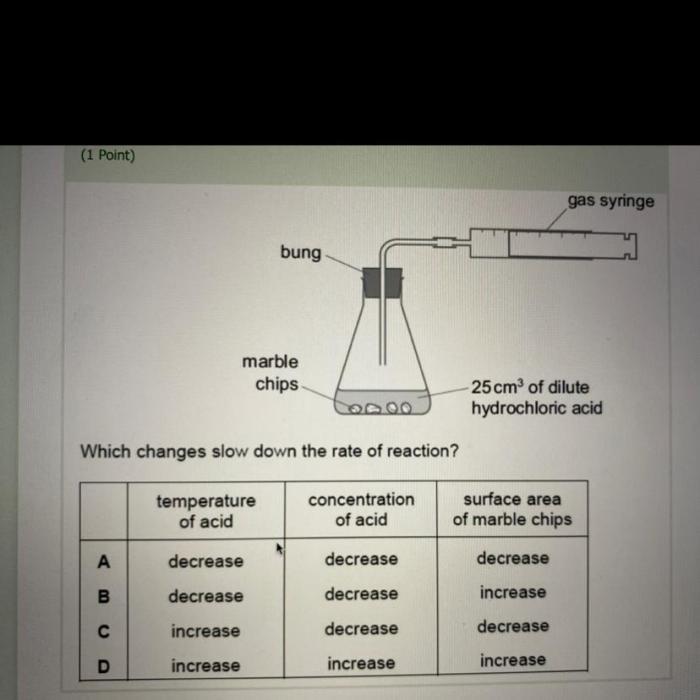
- Concentration of reactants: The rate of a reaction increases with increasing concentration of reactants, as there are more molecules available to collide and react.
- Temperature: The rate of a reaction increases with increasing temperature, as the molecules have more energy and are more likely to overcome the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
- Surface area of reactants: The rate of a reaction increases with increasing surface area of reactants, as there are more molecules exposed to each other and more opportunities for collisions.
- Presence of a catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being consumed in the reaction. Catalysts provide an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur, lowering the activation energy required.
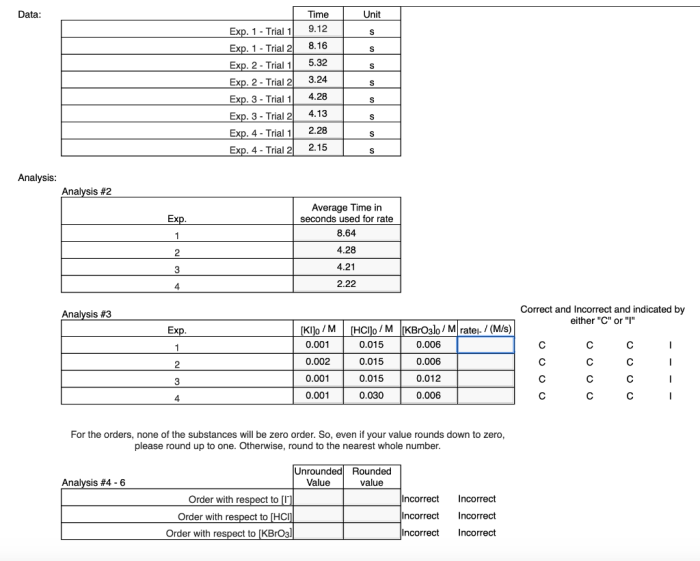
Data Collection and Analysis, Simulation investigating reaction rates answer key
In a simulation, data can be collected by recording the changes in the concentrations of reactants and products over time. Accurate data collection is essential to ensure reliable results.
Statistical techniques, such as linear regression and hypothesis testing, are used to analyze the data and determine the reaction rate. These techniques allow researchers to identify trends and relationships in the data and draw conclusions about the factors that affect the reaction rate.
Simulation Validation
Validation is crucial to ensure that a simulation accurately represents the real-world system it is intended to model. Validation can be performed by comparing the results of the simulation to experimental data or to analytical solutions.
One method of validation is to use a sensitivity analysis, which involves varying the input parameters of the simulation and observing the impact on the output. This analysis helps identify the parameters that have the greatest influence on the simulation results and ensures that the simulation is not overly sensitive to small changes in input.
Applications of Simulation
Simulations are widely used in real-world applications to investigate reaction rates, including:
- Chemical engineering: Simulations are used to design and optimize chemical reactors, ensuring efficient production of desired products.
- Environmental science: Simulations are used to model and predict the fate and transport of pollutants in the environment.
- Biochemistry: Simulations are used to investigate the kinetics of enzymatic reactions and to design new drugs and therapies.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key advantages of using simulation to investigate reaction rates?
Simulation offers several advantages, including the ability to control experimental conditions precisely, eliminate external factors that could confound results, and explore a wide range of scenarios quickly and efficiently.
How can simulation be used to validate experimental findings?
Simulation can be used to validate experimental findings by comparing the predicted results with the observed data. If the simulation accurately predicts the experimental results, it provides strong evidence for the validity of the experimental findings.
What are the limitations of using simulation to investigate reaction rates?
Simulations are limited by the accuracy of the underlying models and the computational resources available. Additionally, simulations may not be able to capture all of the complex interactions that occur in real-world chemical reactions.