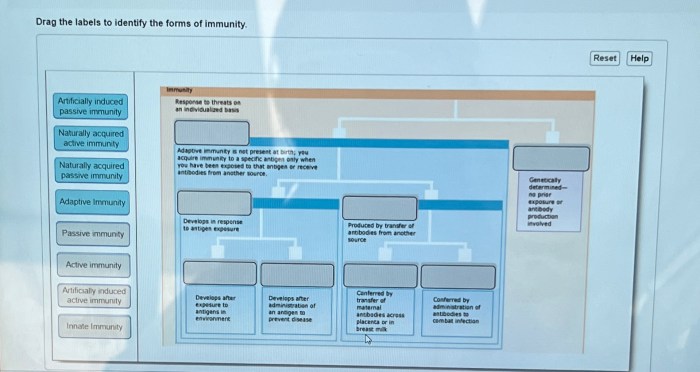
Drag the labels to identify the forms of immunity. This interactive exercise will help you learn about the different types of immunity and how they work together to protect your body from infection. By the end of this exercise, you will be able to identify the different components of the immune system and explain how they work together to keep you healthy.
Innate Immunity
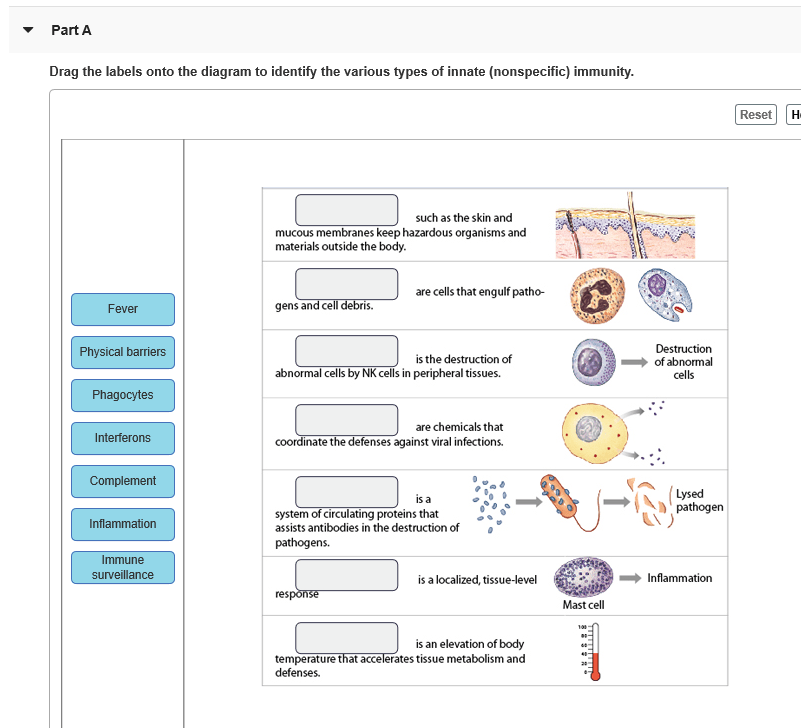
Innate immunity is the body’s first line of defense against infection. It is composed of physical barriers, chemical barriers, and cellular components that work together to prevent pathogens from entering the body and causing disease.
Physical Barriers
- Skin
- Mucous membranes
- Cilia
Chemical Barriers
- Stomach acid
- Lysozyme
- Interferons
Cellular Components
- Neutrophils
- Macrophages
- Natural killer cells
Inflammation and Fever
Inflammation and fever are important parts of the innate immune response. Inflammation helps to recruit immune cells to the site of infection, while fever helps to kill pathogens and slow their growth.
Adaptive Immunity
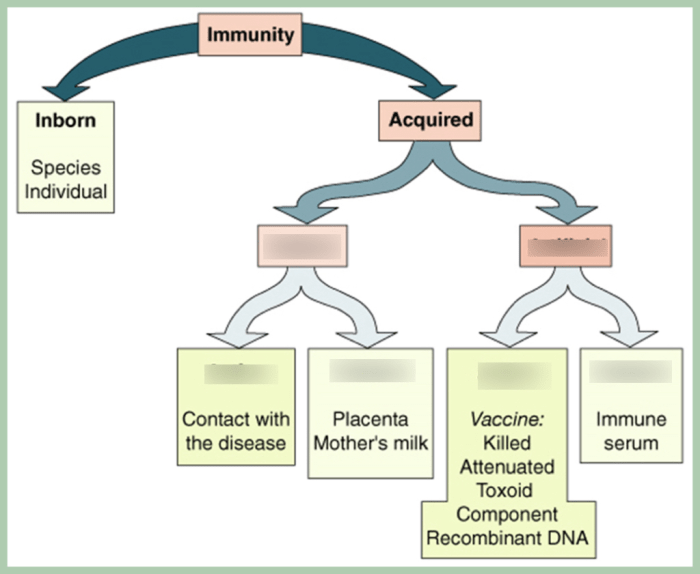
Adaptive immunity is the body’s second line of defense against infection. It is composed of lymphocytes, which are cells that can recognize and attack specific pathogens.
Lymphocytes
- T cells
- B cells
Antigen Presentation and Recognition
Antigens are molecules that are recognized by lymphocytes. When a pathogen enters the body, it is broken down into antigens by antigen-presenting cells. These antigens are then presented to T cells and B cells, which can then recognize and attack the pathogen.
Humoral Immunity
Humoral immunity is a type of adaptive immunity that is mediated by antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that can bind to specific antigens and neutralize them.
Structure and Function of Antibodies
Antibodies are composed of two heavy chains and two light chains. The heavy chains determine the antibody’s specificity for a particular antigen. The light chains help to stabilize the antibody and make it more effective at binding to antigens.
Antibody Production by B Cells
Antibodies are produced by B cells. When a B cell encounters an antigen, it is activated and begins to produce antibodies. The antibodies are then released into the bloodstream, where they can bind to and neutralize antigens.
Cell-Mediated Immunity
Cell-mediated immunity is a type of adaptive immunity that is mediated by T cells. T cells can kill infected cells and help to activate other immune cells.
Types of Cytotoxic T Cells
- CD8+ T cells
- CD4+ T cells
Functions of Cytotoxic T Cells
- Kill infected cells
- Activate other immune cells
- Help to regulate the immune response
Role of Cytokines
Cytokines are proteins that are produced by immune cells. They help to regulate the immune response by signaling to other immune cells.
Immunological Memory: Drag The Labels To Identify The Forms Of Immunity
Immunological memory is the body’s ability to remember past infections and mount a faster and more effective response to future infections. Immunological memory is mediated by memory B cells and memory T cells.
Memory B Cells and Memory T Cells
Memory B cells and memory T cells are long-lived cells that are produced after an infection. They can recognize and attack the same pathogen if it enters the body again.
Importance of Immunological Memory, Drag the labels to identify the forms of immunity
Immunological memory is important because it helps the body to fight off infections more quickly and effectively. This can help to prevent serious illness and death.
Expert Answers
What is the difference between innate and adaptive immunity?
Innate immunity is the body’s first line of defense against infection and is present from birth. Adaptive immunity is a more specialized type of immunity that develops over time as the body is exposed to different pathogens.
What are the different components of the immune system?
The immune system is made up of a variety of cells, tissues, and organs, including the white blood cells, the lymph nodes, the spleen, and the thymus.
How does the immune system protect the body from infection?
The immune system protects the body from infection by identifying and destroying pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
